Getting audit-ready for 49 CFR Part 243: Building a foolproof OJT program
With the passing of the Rail Safety Act in 2008, the Federal Railroad Administration official mandated certain minimum training requirements that applied to safety-related employees working in a railroad, contracted workers, and more.
This opened a new chapter in rail legislation which is undergoing a reckoning as we near a critical deadline within a few months. Because smaller Class II or II railroads have fewer employees, employees may answer to more than one job description, and there are much less resources to devote to building up a program, the FRA pushed out the original 2020 deadline that Class Is had to meet for this specific requirement.
By May 21, 2021, railroads with less than 400,000 annual employee working hours must submit their training programs for 49 CFR Part 243 compliance to the FRA for approval.
American Short Line and Regional Railroad Association (ASLRRA) has been instrumental in pushing for this extension, and are soon releasing FRA-approved training templates that can be incorporate in your OJT program.
With limited time on the horizon before the submission deadline, railroads must plan and implement their on-the-job training and qualification management programs to meet the requirements of the mandate. In this blog post, we’ve outlined some essentials to include in your OJT program, as well as tips to effectively managing OJT training to not only meet bare minimum compliance, but effectively use OJT data to operate safer and smarter.
Some insights into 49 CFR Part 243
The Part 243 mandate outlines high-level instructions for the training and qualification management of safety-related employees in rail transportation companies. In a nutshell, the mandate requires that:
- All safety-related workers and employees should be trained and qualified appropriately to meet minimum FRA training standards.
Insight: Of course, you’ll need to check the box when it comes to meeting training standards. But long-term, you’ll need to be able to monitor and access where training standards are being met, or whether additional trainings should be required based on various factors.
- Employers such as railroads, contractors, and MoW organizations need to submit their training programs for individual schemes to the FRA for approval
Insight: Having the pre-approved Part 243 templates from the ASLRRA will be key to this. But employers will also need to build out a sustainable program that not only meets bare-minimum requirements, but can ensure efficient, effective training.
- Employees should be trained with measurable standards, including OJT programs corresponding to the proposed training programs.
Insight: Employers will be tasked to not only conduct needed training, but measure effectiveness of the training programs and adjust as needed.
- Railroad carriers, contractors, and MoW organizations must maintain training records and submit them to the FRA whenever asked for or during periodic audits
Insight: This means that employers will need to conduct effective record-keeping.
The goal behind this mandate is to ensure that the employees have the knowledge and skills to perform their appointed tasks appropriately and safely. This means that:
- Trainees are instructed to work in an actual work environment using real equipment.
- Trainees are meant to receive instructions and guidance from an experienced mentor present at the work location.
- There should be a repetition of assigned tasks in different conditions to have a varied experience
- Inspections should be carried out to determine the performance levels of employees
All these requirements are essential to OJT training and ensure the desired outcomes from the program: Streamlined onboarding of new employees, safety, efficiency and reliability in operations, employee retention and development, and—most importantly—compliance with 49 CFR Part 243.
The requirements of a compliant, OJT program
If you’re looking at the bare bones of check-box compliance, then there are various requirements that will need to fit into your OJT program.
Classification of safety-related employees: Companies need to classify all safety-related workers and employees dispensing duties on tracks, yards, and trains, including the supervisors, specialists, and crew members.
Definition of roles and responsibilities: There should be a proper definition of roles for each safety-related specialization as a part of your OJT program. These roles must be unique for each different class of railroads and employees should be responsible for the tasks included in their roles.
Templates for individual, safety-related specializations: 49 CFR Part 243 requires the development of individual training program templates for safety-related crafts, such as the handling a certain part of a train, or the usage different specialized equipment.
Training records for FRA as well as internal audits: Railroads must maintain compliance documentation for their OJT programs, be able to record training results, and store records and retrieve records as needed.
Strategies for an effective on-the-job (OJT) training program
As a rail technology partner, we don’t need to tell you have to be compliant. However, we have been able to help our customers implement solutions that not only help them meet compliance, but exceed when it comes to business efficiencies. Companies need to think of extra ways to standardize the training programs in order to get more benefits from it, spend less valuable man-hours doing manual tasks like data entry, and retrieve electronic records quickly.
OJT systems are meant to help railroad organizations effectively achieve the desired outputs to their training and safety programs. But when led by technology, they have the potential to increase the safety factors by a significant amount. Even better if the application is cloud-based, since this can be a cost-effective alternative to paper-based OJT management.
You can learn more about effective on-the-job training strategies in this blog post.
There are many ways in which a technologically-enhanced OJT program can benefit our employees and organization. The main 6 features that should be included in your OJT system are:
- Configuration of training task lists and checklists
Your OJT system should allow you to control different aspects of your training schedules. It should feature the configuration of training tasks according to the different categories of employees as well as enable you to maintain checklists according to your requirements.
- Detailed view of inspection checklists
OJT systems should enable you to manage checklists for each employee and provide you a detailed view of the same. Different checklists for various job specializations should be made available for the execution of programs.
- Mobile tracking and offline mode
The system should be made available offline as well as operable remotely by moving it to the cloud. It would make assessing reports easier for remote and offline supervisors, ensure secure storage of training and employee-related data, and provide system reliability.
- Post-training workflows
The OJT system should be able to provide post-training workflows for individual employees based on their training outcomes. This leads to greater training effectiveness.
- Integration with CRM and HRMS systems
It should feature seamless integration with crew management, qualification tracking, CRM, and HRMS applications to ensure organization-wide data consistency.
- Analytics dashboards
It should also feature detailed analytics and business intelligence dashboards containing compliance reports and information based on training programs. This gives you valuable insights into the training of employees and quick generation of compliance and audit reports.
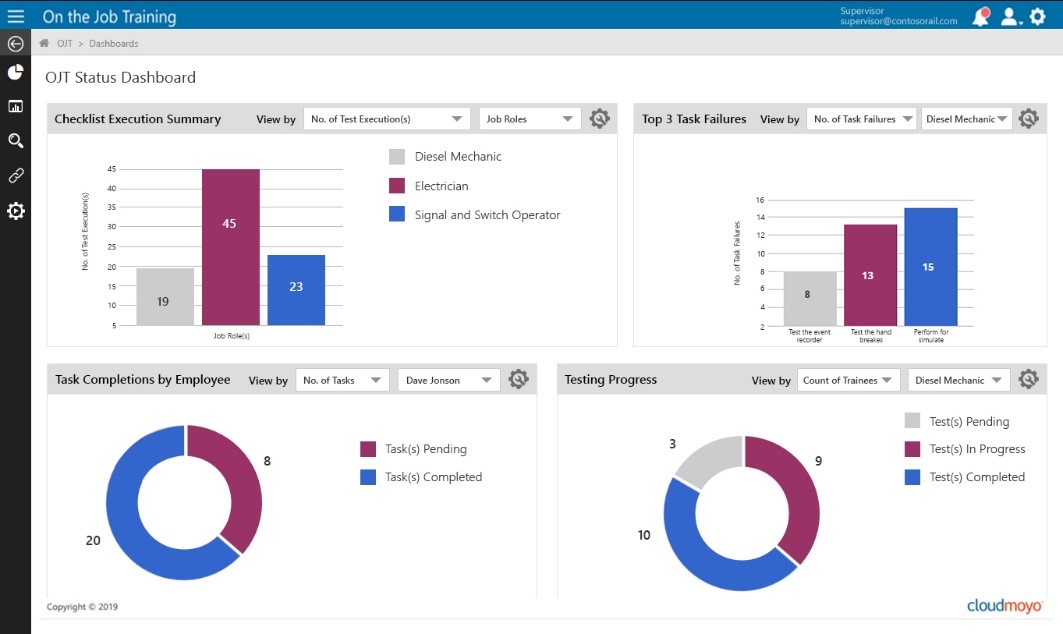
Sample Power BI dashboard visualizing data around training program performance and status
Conclusion
The introduction of 49 CFR Part 243 has made it important for the organizations to ensure compliant and effective training procedures for their safety-related employees. But if you look at this from simply a check-box perspective, then you miss out on the opportunity to deliver customized, performance-based training to your employees, and reduce the risk of safety incidents through close monitoring of training performance.
This requires compliance from training programs that develop skilled employees, and avoid accidentally assigning employees to jobs that they are not qualified for due to missing or expired training credentials.
Need help building out your OJT program? You can learn more about our digital OJT application here, or talk to one of our rail experts to see how we can help.
Live webinar
Opportunities for digitalization in railroad contract management
Date: Tuesday, December 8, 2020 | Time: 10 am PST
![]()
CloudMoyo empowers rail and transportation companies to gain greater insights, unlock efficiencies, and improve agility in operations, revenue and asset management as well as critical areas of safety, crew scheduling and maintenance. Combined with deep rail industry expertise, our cloud-based, AI-driven solutions leverage cutting edge technology to reimagine railroad digitization.
14711 NE 29th Pl, Suite 111, Bellevue, WA – 98007 U.S.
